从互联网(或可信镜像仓库库以外的任何地方)拉取未知镜像会带来风险——例如恶意软件。但是还有其他很好的理由来维护单一的可信来源,例如在企业中实现可支持性。通过确保镜像仅来自受信任的镜像仓库,可以密切控制镜像库存,降低软件熵和蔓延的风险,并提高集群的整体安全性。除此以外,有时还会需要检查镜像的 tag,比如禁止使用 latest 镜像。
这今天我们尝试用“策略即代码”的实现 OPA 来实现功能。
还没开始之前可能有人会问:明明可以实现个 Admission Webhook 就行,为什么还要加上 OPA?
确实可以,但是这样策略和逻辑都会耦合在一起,当策略需要调整的时候需要修改代码重新发布。而 OPA 就是用来做解耦的,其更像是一个策略的执行引擎。
什么是 OPA
Open Policy Agent(以下简称 OPA,发音 “oh-pa”)一个开源的通用策略引擎,可以统一整个堆栈的策略执行。OPA 提供了一种高级声明性语言(Rego),可让你将策略指定为代码和简单的 API,以从你的软件中卸载策略决策。你可以使用 OPA 在微服务、Kubernetes、CI/CD 管道、API 网关等中实施策略。
Rego 是一种高级的声明性语言,是专门为 OPA 建立的。更多 OPA 的介绍可以看 Open Policy Agent 官网,不想看英文直接看这里。
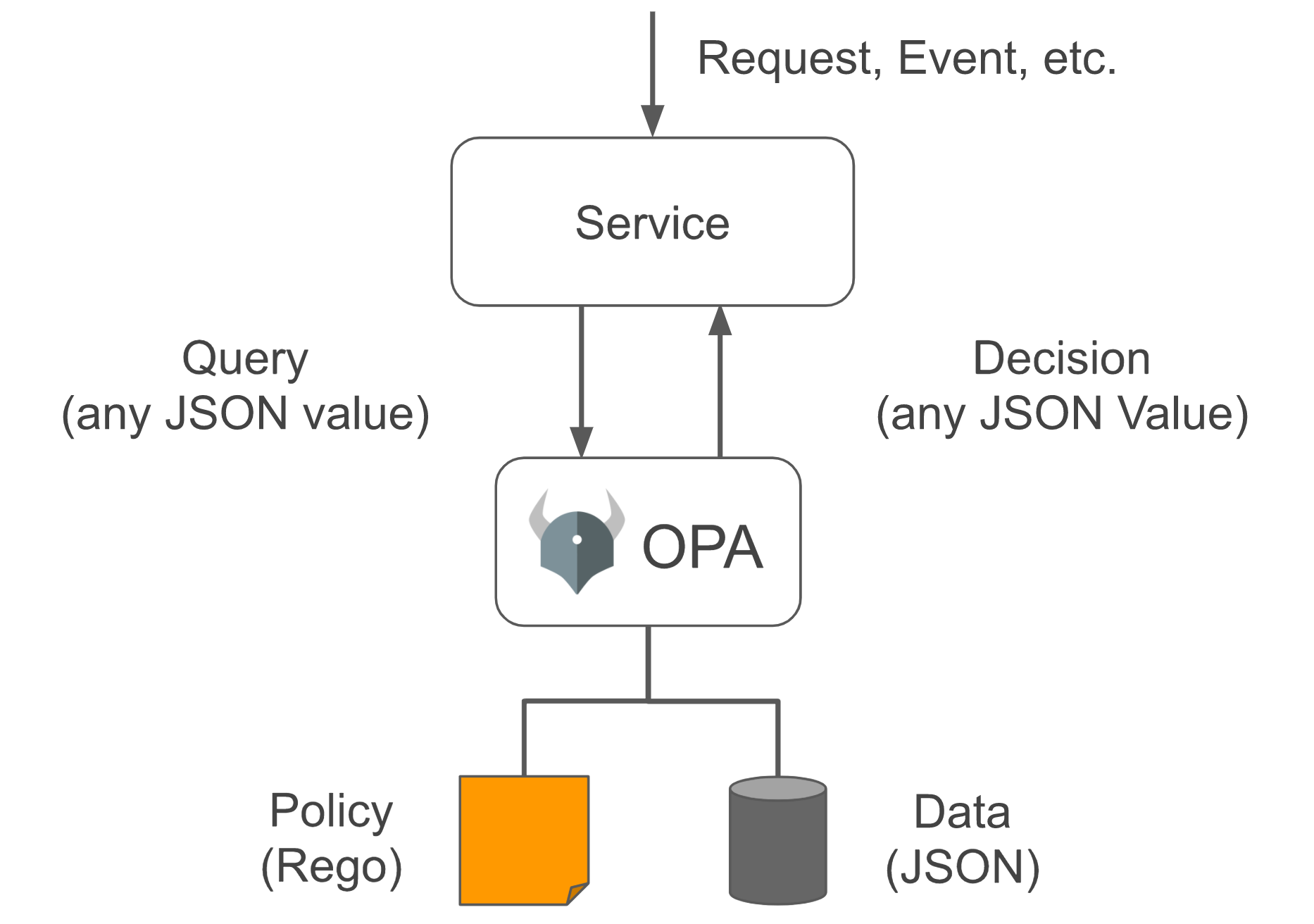
现在进入正题。
启动集群
启动 minikube
minikube start
创建用于部署 OPA 的命名空间
创建并切换到命名空间 opa (命名空间的切换使用 kubens,更多工具介绍见这里)
kubectl create namespace opa
kubens opa
在 Kubernetes 上部署 OPA
Kubernetes 和 OPA 间的通信必须使用 TLS 进行保护。配置 TLS,使用 openssl 创建证书颁发机构(certificate authority CA)和 OPA 的证书/秘钥对。
openssl genrsa -out ca.key 2048
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key ca.key -days 100000 -out ca.crt -subj "/CN=admission_ca"
为 OPA 创建 TLS 秘钥和证书:
cat >server.conf <<EOF
[req]
req_extensions = v3_req
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
prompt = no
[req_distinguished_name]
CN = opa.opa.svc
[ v3_req ]
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
extendedKeyUsage = clientAuth, serverAuth
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
DNS.1 = opa.opa.svc
EOF
注意
CN和alt_names必须与后面创建 OPA service 的匹配。
openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048
openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr -config server.conf
openssl x509 -req -in server.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -out server.crt -days 100000 -extensions v3_req -extfile server.conf
为 OPA 创建保存 TLS 凭证的 Secret:
kubectl create secret tls opa-server --cert=server.crt --key=server.key
将 OPA 部署为准入控制器(admission controller)。
admission-controller.yaml:
# 授权 OPA/kube-mgmt 对资源的只读权限
# kube-mgmt 会同步资源信息给 OPA,以便在策略中使用
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: opa-viewer
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: view
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts:opa
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
# 为 OPA/kube-mgmt 定义角色来在 configmaps 中更新策略状态
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: opa
name: configmap-modifier
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["update", "patch"]
---
# 为 OPA/kube-mgmt 授予角色
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: opa
name: opa-configmap-modifier
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: configmap-modifier
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts:opa
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: opa
namespace: opa
spec:
selector:
app: opa
ports:
- name: https
protocol: TCP
port: 443
targetPort: 8443
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: opa
namespace: opa
name: opa
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: opa
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: opa
name: opa
spec:
containers:
# WARNING: OPA is NOT running with an authorization policy configured. This
# means that clients can read and write policies in OPA. If you are
# deploying OPA in an insecure environment, be sure to configure
# authentication and authorization on the daemon. See the Security page for
# details: https://www.openpolicyagent.org/docs/security.html.
- name: opa
image: openpolicyagent/opa:0.30.1-rootless
args:
- "run"
- "--server"
- "--tls-cert-file=/certs/tls.crt"
- "--tls-private-key-file=/certs/tls.key"
- "--addr=0.0.0.0:8443"
- "--addr=http://127.0.0.1:8181"
- "--log-format=json-pretty"
- "--set=decision_logs.console=true"
volumeMounts:
- readOnly: true
mountPath: /certs
name: opa-server
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health?plugins&bundle
scheme: HTTPS
port: 8443
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 5
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
scheme: HTTPS
port: 8443
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 5
- name: kube-mgmt
image: openpolicyagent/kube-mgmt:0.11
args:
- "--replicate=v1/pods"
volumes:
- name: opa-server
secret:
secretName: opa-server
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: opa-default-system-main
namespace: opa
data:
main: |
package system
import data.kubernetes.validating.images
main = {
"apiVersion": "admission.k8s.io/v1beta1",
"kind": "AdmissionReview",
"response": response,
}
default uid = ""
uid = input.request.uid
response = {
"allowed": false,
"uid": uid,
"status": {
"reason": reason,
},
} {
reason = concat(", ", images.deny)
reason != ""
}
else = {"allowed": true, "uid": uid}
kubectl apply -f admission-controller.yaml
接下来,生成将用于将 OPA 注册为准入控制器的 manifest。
cat > webhook-configuration.yaml <<EOF
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: opa-validating-webhook
webhooks:
- name: validating-webhook.openpolicyagent.org
rules:
- operations: ["CREATE", "UPDATE"]
apiGroups: ["*"]
apiVersions: ["*"]
resources: ["pods"]
clientConfig:
caBundle: $(cat ca.crt | base64 | tr -d '\n')
service:
namespace: opa
name: opa
EOF
生成的配置文件包含 CA 证书的 base64 编码,以便可以在 Kubernetes API 服务器和 OPA 之间建立 TLS 连接。
kubectl apply -f webhook-configuration.yaml
查看 OPA 日志:
kubectl logs -l app=opa -c opa -f
定义策略并通过 Kubernetes 将其加载到 OPA
这里我们定义了对容器镜像的检查:
- 是否来自受信任的仓库
- 是否使用了 latest tag 的镜像
image-policy.rego
package kubernetes.validating.images
deny[msg] {
some i
input.request.kind.kind == "Pod"
image := input.request.object.spec.containers[i].image
endswith(image, ":latest")
msg := sprintf("Image '%v' used latest image", [image])
} {
some i
input.request.kind.kind == "Pod"
image := input.request.object.spec.containers[i].image
not startswith(image, "192.168.64.1:5000")
msg := sprintf("Image '%v' comes from untrusted registry", [image])
}
kubectl create configmap image-policy --from-file=image-policy.rego
检查 configmap 的 annotation openpolicyagent.org/policy-status 值是否 为 '{"status":"ok"}'。否则,就要根据报错信息处理问题。
注:192.168.64.1:5000 是笔者本地容器运行的一个私有仓库。
version: '3.6'
services:
registry:
image: registry:2.7.1
container_name: registry
restart: always
environment:
REGISTRY_HTTP_ADDR: 0.0.0.0:5000
REGISTRY_STORAGE: filesystem
REGISTRY_STORAGE_DELETE_ENABLED: 'true'
REGISTRY_STORAGE_FILESYSTEM_ROOTDIRECTORY: /var/lib/registry
ports:
- '5000:5000'
volumes:
- '/Users/addo/Downloads/tmp/registry:/var/lib/registry'
测试
pod-bad-repo.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
run: web-server
name: web-server
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:1.21.1
name: web-server
resources: {}
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
status: {}
kubectl apply -f pod-bad-repo.yaml
Error from server (Image 'nginx:1.21.1' comes from untrusted registry): error when creating "pod-bad-repo.yaml": admission webhook "validating-webhook.openpolicyagent.org" denied the request: Image 'nginx:1.21.1' comes from untrusted registry
pod-bad-tag.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
run: web-server
name: web-server
spec:
containers:
- image: 192.168.64.1:5000/nginx:latest
name: web-server
resources: {}
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
status: {}
kubectl apply -f pod-bad-tag.yaml
Error from server (Image '192.168.64.1:5000/nginx:latest' used latest image): error when creating "pod-bad-tag.yaml": admission webhook "validating-webhook.openpolicyagent.org" denied the request: Image '192.168.64.1:5000/nginx:latest' used latest image
pod-ok.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
run: web-server
name: web-server
spec:
containers:
- image: 192.168.64.1:5000/nginx:1.21.1
name: web-server
resources: {}
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
status: {}
kubectl apply -f pod-ok.yaml
pod/web-server created
总结
策略即代码,以代码的实现表达策略;在通过策略与执行引擎的解耦分离,让策略更加的灵活。
后面我们再探索 OPA 的更多场景。